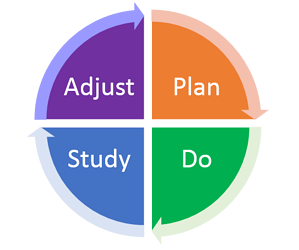
- The PDSA cycle of quality improvement, sometimes called the “Deming Cycle,” is based on the scientific method, which approaches problems through hypothesis (plan), experimentation (do), and evaluation (study).
- In business, the output of a successful PDSA cycle is a new standard work that institutionalizes the improvement.
1. Plan :
- The planning step must include answers to the following questions:
- What are we trying to accomplish?
- Do we understand the problem and the current situation?
- How will we know if the change is an improvement?
- What changes can we make that will result in improvement?
- Who should be involved in the project?
- What are the dates and milestones associated with this work?
2. Do :
- Once the planning phase is complete and a hypothesis has been made about specific changes expected to lead to measurable improvement, the “do” step can begin.
- This part of the cycle should be considered experimental.
- As with a scientific experiment, careful observation and data collection are just as important as the action itself.
3. Study:
- Teams commonly use control charts to visualize the results of the process over time.
- They can help sort out standard (expected) variation in results from special cause (unexpected) variation.
4. Adjust:
- This is when it is time to communicate the change with all stakeholders and recognize the efforts of those who participated in the work.
- PDSA in quality improvement can be used to identify new standards that constantly improve process results and, therefore, customer value
To know more about this method of scaling a business, do read the entire article:https://blog.kainexus.com/continuous-improvement/improvement-disciplines/lean/pdsa/a-scientific-approach-to-continuous-improvement
We’re here and we’re listening to your questions. Do follow this link to get all your entrepreneurial doubts cleared at a one-step Q&A panel with our experts: https://sncoglobal.com/#q&a
Share: